
“The Evolution of Computer Technology: From Mainframes to Cloud Computing
Related Articles The Evolution of Computer Technology: From Mainframes to Cloud Computing
Introduction
On this special occasion, we are happy to review interesting topics related to The Evolution of Computer Technology: From Mainframes to Cloud Computing. Come on knit interesting information and provide new insights to readers.
The Evolution of Computer Technology: From Mainframes to Cloud Computing
The world hums with the quiet power of interconnected devices, a symphony orchestrated by the evolution of computer technology. From the behemoths that filled entire rooms to the invisible infrastructure powering our smartphones, the journey has been nothing short of breathtaking. This evolution, from the era of mainframes to the ubiquitous cloud, is not just a technological marvel; it’s a story deeply intertwined with societal progress, economic growth, and the very fabric of modern life. Understanding this evolution is crucial, not only to appreciate the present but also to anticipate the future of computing.
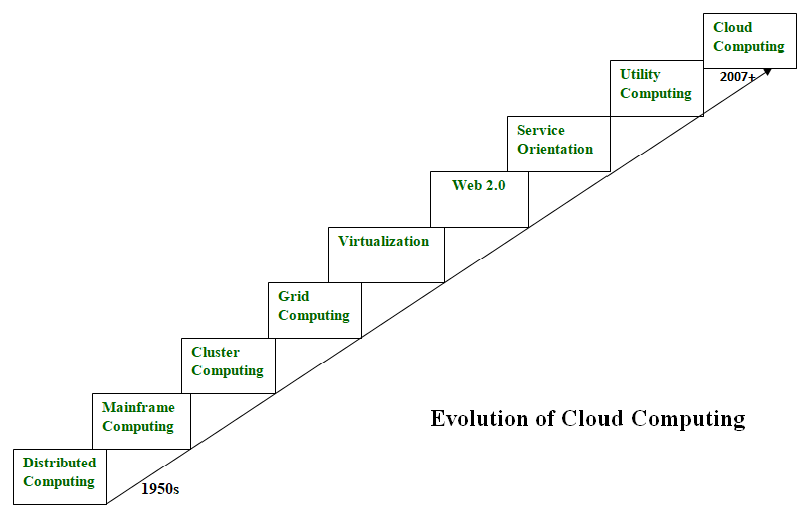
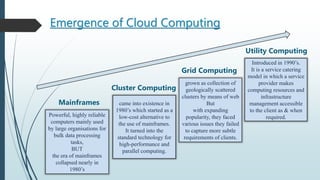
The Dawn of the Mainframe Era: Giants of Computation
The mid-20th century witnessed the birth of the mainframe computer, a monumental achievement in engineering and a cornerstone of early computing. These colossal machines, often occupying entire rooms and requiring specialized cooling systems, were the undisputed kings of processing power. IBM, with its System/360 series, dominated this landscape. Mainframes were characterized by their centralized architecture, with all processing, storage, and input/output operations handled by a single, powerful machine. They served as the backbone of large organizations, powering critical applications in government, finance, and research. Think of the Apollo 11 moon landing; the complex calculations that guided the mission relied heavily on mainframe computing.
The mainframe era, however, presented significant limitations. Access was restricted, typically requiring specialized training and physical proximity to the machine. Cost was prohibitive, making it accessible only to large institutions and corporations. Moreover, the centralized nature made the system vulnerable to single points of failure. A malfunction in the mainframe could bring an entire organization to a standstill. Despite these limitations, the mainframe laid the groundwork for future advancements, introducing fundamental concepts like operating systems and programming languages that continue to shape modern computing.
The Rise of Minicomputers and Personal Computers: Decentralization and Accessibility
The 1960s and 70s witnessed the emergence of minicomputers, smaller and more affordable than mainframes. These machines, while still significantly larger than today’s PCs, brought computing power to smaller organizations and departments within larger ones. Companies like Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) played a pivotal role in popularizing minicomputers. This decentralization marked a crucial shift, allowing for more distributed processing and improved accessibility.
The true revolution, however, came with the personal computer (PC) revolution in the late 1970s and 80s. The introduction of the Altair 8800, Apple II, and IBM PC democratized computing, placing processing power within the reach of individuals and small businesses. This era saw the explosive growth of software applications, fostering innovation across various sectors. The development of graphical user interfaces (GUIs) made computers significantly more user-friendly, further broadening their appeal. This period also witnessed the rise of networking technologies, connecting PCs and enabling data sharing and collaboration.
The Internet and Client-Server Architecture: The Network Effect
The advent of the internet fundamentally changed the landscape of computing. The client-server architecture emerged as a dominant paradigm, with powerful servers handling data storage and processing, while clients (PCs, workstations) accessed these resources through networks. This model enabled the development of sophisticated applications like email, web browsers, and online databases. The internet’s ability to connect diverse systems globally fostered unprecedented levels of collaboration and information sharing. The rise of the World Wide Web in the 1990s dramatically increased the accessibility and usability of the internet, transforming it from a niche technology to a ubiquitous tool.
The Emergence of Cloud Computing: The On-Demand Paradigm
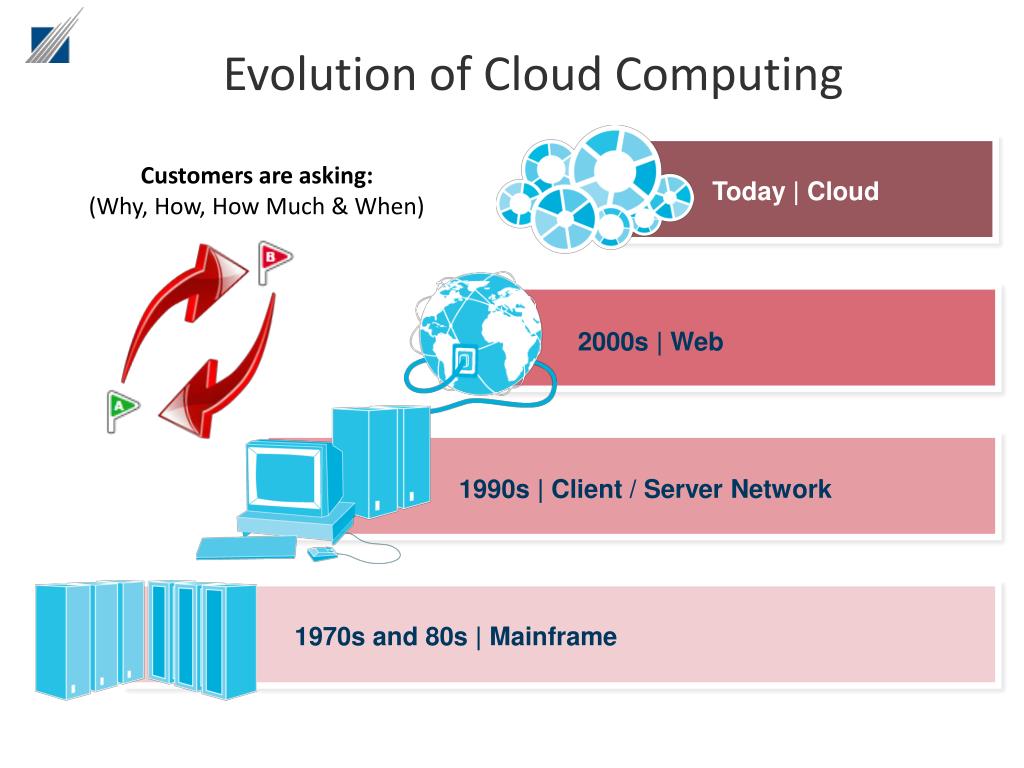
Cloud computing represents the latest, and arguably most significant, evolution in computer technology. It shifts the focus from owning and maintaining physical infrastructure to accessing computing resources – servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence – on demand over the internet. This paradigm offers several key advantages:
- Scalability: Cloud resources can be easily scaled up or down based on demand, eliminating the need for large upfront investments and minimizing wasted resources.
- Cost-effectiveness: Pay-as-you-go models reduce capital expenditures and operational costs, making computing resources accessible to a wider range of users.
- Flexibility and Agility: Cloud computing enables businesses to rapidly deploy new applications and services, adapt to changing market conditions, and respond quickly to evolving customer needs.
- Increased Reliability and Availability: Cloud providers invest heavily in infrastructure redundancy and disaster recovery, ensuring high availability and minimizing downtime.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Cloud platforms facilitate collaboration by enabling multiple users to access and share data and applications simultaneously.

Several models of cloud computing exist, including:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Provides virtualized computing resources, including servers, storage, and networking. Examples include Amazon Web Services (AWS) EC2, Microsoft Azure Virtual Machines, and Google Compute Engine.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): Offers a platform for developing, deploying, and managing applications without the need to manage the underlying infrastructure. Examples include AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Google App Engine, and Heroku.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Delivers software applications over the internet, eliminating the need for local installation and maintenance. Examples include Salesforce, Microsoft 365, and Google Workspace.
Real-world examples of cloud computing’s impact:
- Netflix: Relies heavily on cloud infrastructure to stream movies and TV shows globally, scaling its resources to handle peak demand.
- Airbnb: Uses cloud computing to manage its platform, handling bookings, payments, and customer support for millions of users worldwide.
- Healthcare: Cloud-based solutions are revolutionizing healthcare by enabling remote patient monitoring, secure data storage, and collaborative research.
Actionable Advice for Utilizing Cloud Computing:
- Assess your needs: Carefully evaluate your organization’s computing requirements before selecting a cloud provider and service model.
- Choose the right provider: Consider factors like cost, security, scalability, and compliance requirements when choosing a cloud provider.
- Implement robust security measures: Protect your data and applications by implementing strong security protocols and utilizing cloud provider security features.
- Monitor and optimize your cloud usage: Regularly monitor your cloud resource consumption and optimize your deployments to minimize costs and improve performance.
The Future of Computing: Beyond the Cloud?
The evolution of computer technology is an ongoing process. While cloud computing currently dominates the landscape, future trends suggest further advancements, including:
- Edge computing: Processing data closer to the source (e.g., IoT devices) to reduce latency and bandwidth requirements.
- Quantum computing: Leveraging the principles of quantum mechanics to solve complex problems beyond the capabilities of classical computers.
- Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML): Integrating AI and ML capabilities into various applications to automate tasks, analyze data, and improve decision-making.
The journey from room-sized mainframes to the invisible infrastructure of the cloud is a testament to human ingenuity and our relentless pursuit of technological advancement. The future of computing promises even more transformative changes, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible and reshaping the way we live, work, and interact with the world. The question remains: what innovative technologies will emerge to redefine the landscape of computing in the years to come? And how will we harness their power responsibly and ethically?
Conclusion
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insight into The Evolution of Computer Technology: From Mainframes to Cloud Computing. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!






