
“Technology in Healthcare: From Telemedicine to Robotic Surgery
Related Articles Technology in Healthcare: From Telemedicine to Robotic Surgery
- IoT (Internet Of Things): Building A Connected World
- The Advancements In Cloud Technology: Benefits And Challenges
- The Impact Of Artificial Intelligence On Industry Transformation: A New Era Of Efficiency And Innovation
- What Is Big Data And How Does It Impact Business?
- Understanding The Role Of Blockchain In Digital Security
Introduction
On this special occasion, we are happy to review interesting topics related to Technology in Healthcare: From Telemedicine to Robotic Surgery. Come on knit interesting information and provide new insights to readers.
Technology in Healthcare: From Telemedicine to Robotic Surgery
The whirring of robotic arms performing intricate surgeries, the comforting voice of a doctor on a video screen miles away – these scenes, once relegated to science fiction, are now commonplace realities in the ever-evolving landscape of healthcare. Technology is rapidly transforming how we prevent, diagnose, treat, and manage diseases, ushering in an era of unprecedented precision, accessibility, and efficiency. From the widespread adoption of telemedicine to the sophisticated advancements in robotic surgery, technological innovation is fundamentally reshaping the patient experience and the future of medicine. This revolution isn’t just about gadgets; it’s about improving patient outcomes, increasing efficiency, and expanding access to quality care, especially in underserved areas. Understanding this transformative power is crucial for both healthcare professionals and the general public as we navigate this exciting and rapidly changing field.
Main Body
1. Telemedicine: Bridging the Gap in Healthcare Access
Telemedicine, the remote delivery of healthcare services using technology, has emerged as a game-changer, particularly in addressing geographical barriers and healthcare disparities. Through video conferencing, remote patient monitoring devices, and secure messaging platforms, patients can access consultations, diagnoses, and even ongoing treatment from healthcare providers without the need for physical visits. This is particularly beneficial for patients in rural areas with limited access to specialists, individuals with mobility issues, and those managing chronic conditions requiring frequent monitoring.
For example, the use of telehealth during the COVID-19 pandemic demonstrated its immense potential. Many healthcare systems rapidly expanded their telehealth offerings, allowing patients to safely receive care while minimizing exposure to the virus. Studies showed a significant increase in telehealth utilization, with patients reporting high satisfaction levels with the convenience and accessibility offered. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) also significantly expanded telehealth reimbursement, recognizing its vital role in ensuring continuity of care.
Actionable Advice: If you are considering using telemedicine, research reputable providers and ensure they are licensed and adhere to HIPAA regulations for data privacy and security. Check with your insurance provider to understand coverage for telehealth services.
2. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): Enhancing Diagnostics and Treatment
AI and ML are revolutionizing healthcare through their ability to analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns, predict outcomes, and assist in decision-making. In diagnostics, AI algorithms can analyze medical images (X-rays, CT scans, MRIs) with remarkable accuracy, detecting subtle anomalies that might be missed by the human eye. This can lead to earlier and more accurate diagnoses, improving patient outcomes and reducing healthcare costs.
For instance, AI-powered tools are being used to detect cancerous tumors in mammograms with greater sensitivity and specificity than human radiologists alone. Similarly, AI algorithms are being developed to predict patient risk for various conditions, such as heart failure or stroke, allowing for proactive interventions and preventive measures.
Actionable Advice: While AI is transforming healthcare, it’s crucial to remember that it’s a tool to assist healthcare professionals, not replace them. Transparency and explainability in AI algorithms are essential to ensure trust and accountability.
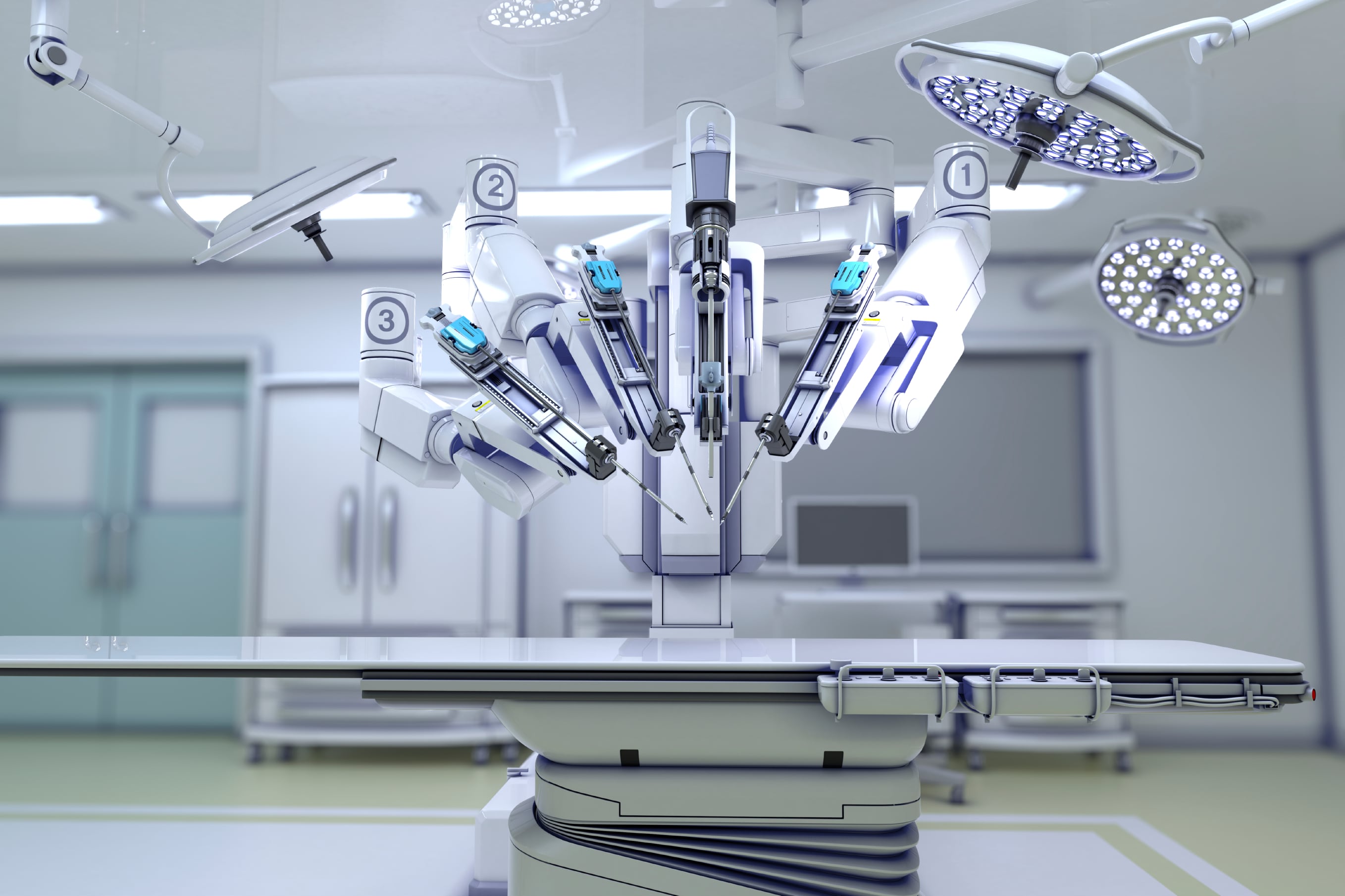
3. Robotic Surgery: Minimally Invasive Precision
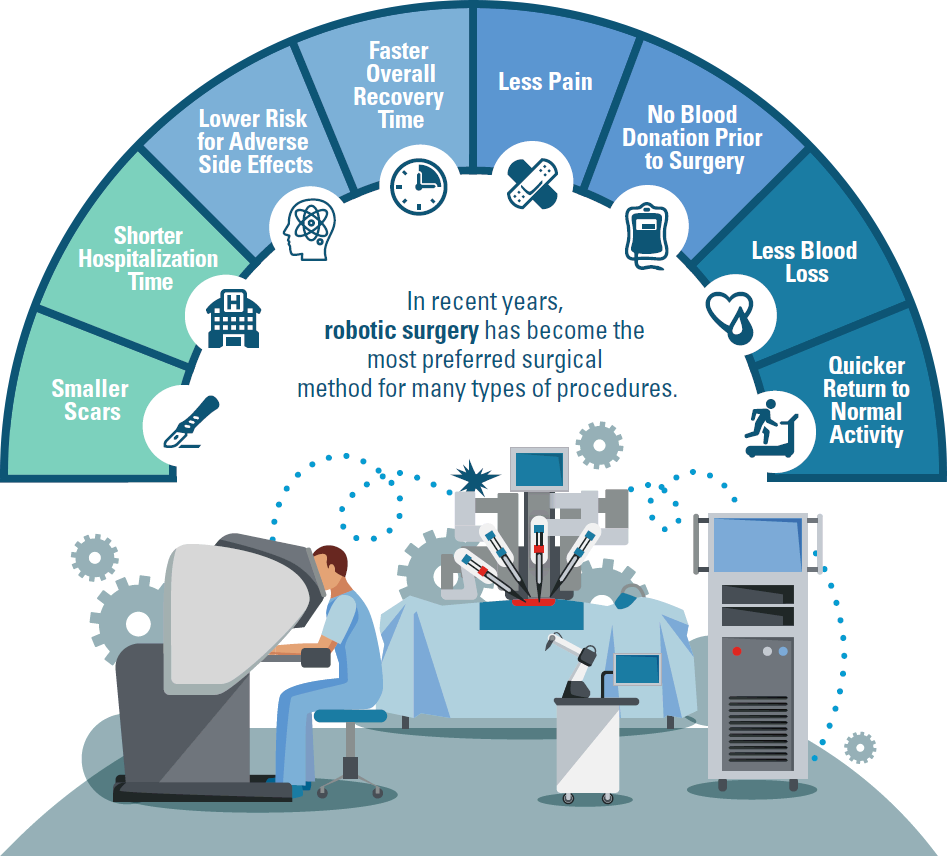
Robotic surgery, using robotic systems controlled by surgeons, has transformed minimally invasive procedures. These systems offer enhanced dexterity, precision, and control compared to traditional laparoscopic techniques, resulting in smaller incisions, reduced pain, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery times. Robotic surgery is particularly valuable in complex procedures requiring high precision, such as cardiac surgery, urological procedures, and gynecological surgeries.
The da Vinci Surgical System is a prime example of a widely used robotic surgical system. Its advanced features, including 3D high-definition vision and wristed instruments, allow surgeons to perform intricate maneuvers with greater accuracy and control. Studies have shown that robotic surgery can lead to reduced blood loss, fewer complications, and improved cosmetic outcomes compared to open surgery.
Actionable Advice: If you are considering robotic surgery, discuss the procedure thoroughly with your surgeon to understand the benefits, risks, and alternatives. Ask about the surgeon’s experience with the specific robotic system and the type of procedure.
4. Wearable Technology and Remote Patient Monitoring: Empowering Patients

Wearable technology, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, is increasingly used for remote patient monitoring (RPM). These devices can track vital signs like heart rate, blood pressure, and activity levels, providing valuable data to healthcare providers. This continuous monitoring allows for early detection of potential health problems, enabling timely interventions and preventing hospitalizations.
For patients with chronic conditions like heart failure or diabetes, RPM can significantly improve management and outcomes. For example, continuous glucose monitors can provide real-time glucose data, enabling patients and their healthcare providers to make informed decisions about insulin adjustments. Similarly, wearable cardiac monitors can detect irregular heart rhythms, alerting patients and doctors to potential cardiac events.
Actionable Advice: If you are considering using wearable technology for health monitoring, choose devices that are FDA-approved and compatible with your healthcare provider’s system. Understand the data collected and how it will be used to inform your care.
5. 3D Printing in Healthcare: Revolutionizing Prosthetics and Implants
3D printing technology is transforming healthcare by enabling the creation of customized medical devices, prosthetics, and implants. This personalized approach allows for a better fit, improved functionality, and enhanced patient comfort. 3D printing is also used to create anatomical models for surgical planning, allowing surgeons to practice complex procedures before operating on patients.
For example, 3D-printed prosthetics are becoming increasingly sophisticated, offering greater functionality and natural movement. 3D-printed implants can be customized to fit the patient’s unique anatomy, reducing the risk of complications and improving integration with the body.
Actionable Advice: While 3D printing is advancing rapidly, it’s important to ensure that any 3D-printed medical device or implant is manufactured by a reputable company adhering to safety and regulatory standards.
6. Big Data Analytics: Improving Healthcare Efficiency and Outcomes
The massive amounts of healthcare data generated daily – from electronic health records to genomic information – present both challenges and opportunities. Big data analytics tools allow healthcare organizations to analyze this data to identify trends, improve efficiency, and optimize resource allocation. This can lead to better patient care, reduced costs, and improved public health outcomes.
For example, big data analytics can be used to predict hospital readmissions, identify patients at high risk for certain conditions, and optimize staffing levels. By analyzing patient data, healthcare systems can identify areas for improvement in care delivery and develop more effective treatment strategies.
Actionable Advice: While big data analytics offers immense potential, it’s crucial to address concerns about data privacy and security. Robust data protection measures are essential to ensure patient confidentiality and prevent misuse of sensitive information.
Conclusion
The integration of technology into healthcare is not just a trend; it’s a fundamental shift in how we approach health and well-being. From telemedicine’s expansion of access to the precision of robotic surgery and the analytical power of AI, technology is enhancing the quality, efficiency, and accessibility of healthcare services. While challenges remain, particularly regarding data security, affordability, and equitable access, the potential benefits are immense. As we move forward, it’s crucial to prioritize ethical considerations, patient safety, and responsible innovation to ensure that technology serves as a powerful tool to improve health outcomes for all. The question remains: how can we best harness the transformative power of technology to create a truly equitable and accessible healthcare system for the future?

Conclusion
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insight into Technology in Healthcare: From Telemedicine to Robotic Surgery. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!






