
“Understanding the Role of Blockchain in Digital Security
Related Articles Understanding the Role of Blockchain in Digital Security
- The Advancements In Cloud Technology: Benefits And Challenges
- What Is Big Data And How Does It Impact Business?
- The Evolution Of Computer Technology: From Mainframes To Cloud Computing
Introduction
We will be happy to explore interesting topics related to Understanding the Role of Blockchain in Digital Security. Come on knit interesting information and provide new insights to readers.
Understanding the Role of Blockchain in Digital Security
In a world increasingly reliant on digital interactions, security concerns loom large. From data breaches targeting personal information to sophisticated cyberattacks crippling critical infrastructure, the threat landscape is constantly evolving. This necessitates a robust and resilient approach to digital security. Enter blockchain technology, a revolutionary system that promises to reshape our understanding of security and trust in the digital realm. While often associated with cryptocurrencies, blockchain’s potential extends far beyond financial applications. Its inherent security features offer a powerful toolkit for safeguarding sensitive data, enhancing authentication processes, and building more trustworthy digital ecosystems. This article delves into the multifaceted role of blockchain in bolstering digital security, exploring its applications and limitations.
Immutable Records: The Foundation of Blockchain Security
At the heart of blockchain’s security lies its immutable ledger. Data, once recorded on a blockchain, cannot be altered or deleted without detection. This immutability stems from the decentralized and distributed nature of the system. Instead of being stored in a single, vulnerable location, blockchain data is replicated across a network of computers (nodes). Any attempt to modify the data requires altering the records on a majority of these nodes, a practically impossible task given the distributed and cryptographic nature of the system. This inherent tamper-proof characteristic makes blockchain ideal for securing sensitive information, such as medical records, intellectual property rights, and supply chain data. For example, a pharmaceutical company could use a blockchain to track the movement of drugs throughout the supply chain, ensuring authenticity and preventing counterfeiting. The immutable record of each transaction provides irrefutable proof of origin and handling, minimizing the risk of fraudulent activities.
Enhanced Data Integrity and Transparency
Blockchain’s transparency further enhances its security capabilities. All transactions are recorded publicly and cryptographically linked, creating a verifiable chain of events. This transparency allows for real-time auditing and monitoring, making it easier to detect anomalies and potential security breaches. For instance, in the voting process, a blockchain-based system could provide verifiable and auditable records of each vote cast, reducing the risk of manipulation and increasing voter confidence. Similarly, in the management of digital identities, blockchain can offer a secure and transparent way to verify identities, reducing the risk of identity theft and fraud.
Decentralization: Mitigating Single Points of Failure
Traditional centralized systems are vulnerable to single points of failure. If a central server is compromised, the entire system is at risk. Blockchain’s decentralized architecture mitigates this risk. The distributed nature of the ledger eliminates the reliance on a single authority, making it far more resilient to attacks. Even if some nodes are compromised, the remaining nodes continue to operate, ensuring the integrity of the system. This resilience is particularly crucial for applications requiring high availability and fault tolerance, such as critical infrastructure management and financial transactions.
Cryptographic Security: Protecting Data in Transit and at Rest
Blockchain leverages sophisticated cryptographic techniques to secure data both in transit and at rest. Cryptography ensures the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of data. For example, using public-key cryptography, users can securely share information without revealing their private keys. The use of hashing algorithms further ensures data integrity, as any alteration to the data will result in a different hash value, instantly revealing tampering. This cryptographic foundation is crucial for protecting sensitive data and preventing unauthorized access.
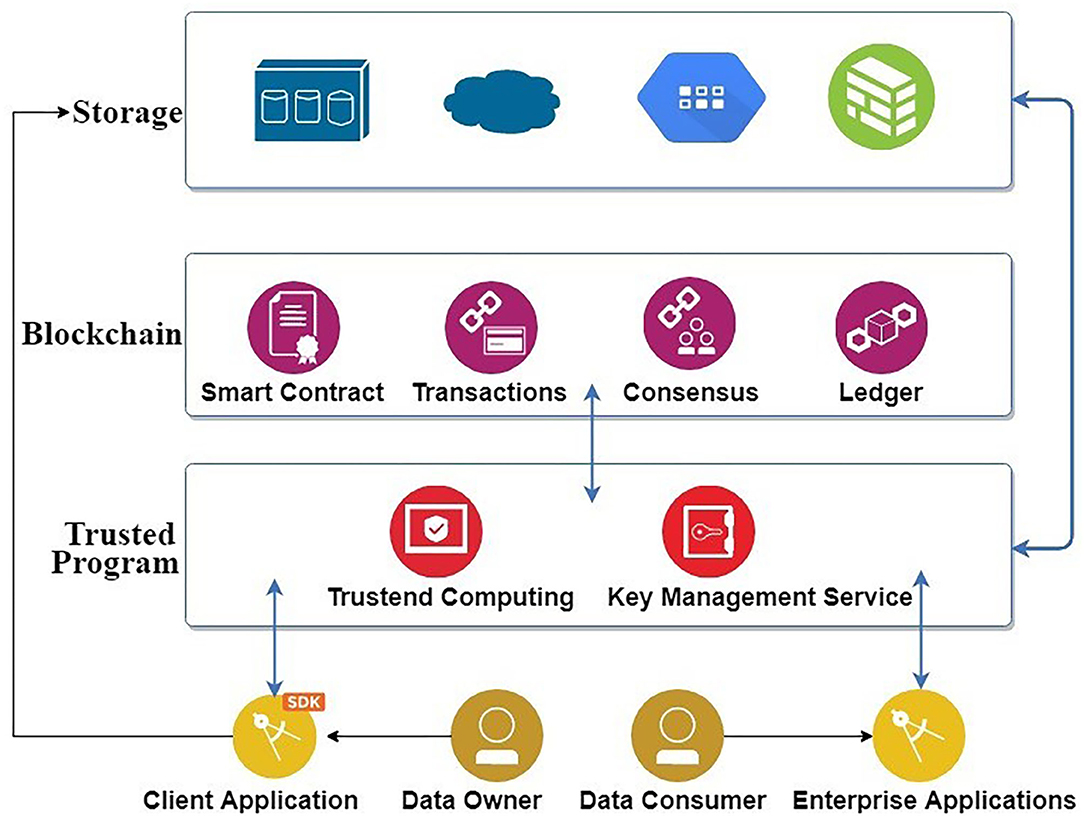
Smart Contracts: Automating Secure Transactions
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. They automate transactions and enforce agreements without the need for intermediaries, reducing the risk of fraud and human error. For example, in supply chain management, smart contracts can automatically trigger payments upon delivery of goods, ensuring timely and secure transactions. In insurance, smart contracts can automate claims processing, reducing delays and improving efficiency. The immutability and transparency of blockchain ensure that smart contracts are executed as intended, enhancing the security and reliability of transactions.
Challenges and Limitations of Blockchain in Digital Security
While blockchain offers significant advantages in digital security, it’s crucial to acknowledge its limitations. The complexity of implementing and managing blockchain systems can be a barrier for some organizations. The energy consumption associated with some blockchain networks, particularly those using Proof-of-Work consensus mechanisms, is a significant environmental concern. Furthermore, the security of a blockchain system is only as strong as its weakest link. Vulnerabilities in the underlying code or in the implementation of the system can still be exploited by malicious actors. Finally, the regulatory landscape surrounding blockchain technology is still evolving, creating uncertainty for some applications.
Real-World Examples of Blockchain in Digital Security
Several real-world examples demonstrate blockchain’s impact on digital security:

- Supply Chain Management: Companies like Walmart are using blockchain to track the origin and movement of food products, enhancing transparency and traceability, and reducing the risk of foodborne illnesses.
- Healthcare: MedicalChain is developing a blockchain-based platform for secure storage and sharing of medical records, improving patient privacy and data integrity.
- Digital Identity: Several projects are exploring the use of blockchain for secure digital identity management, reducing the risk of identity theft and fraud.
- Voting Systems: Some countries are exploring the use of blockchain for secure and transparent voting systems, enhancing voter confidence and reducing the risk of election manipulation.

Actionable Advice for Enhancing Digital Security with Blockchain
While implementing a full-scale blockchain solution may not be feasible for all organizations, several steps can be taken to leverage its security benefits:
- Identify critical data: Determine which data assets require the highest level of security and explore the feasibility of using blockchain for their protection.
- Assess existing infrastructure: Evaluate your current IT infrastructure and determine its compatibility with blockchain technology.
- Choose the right blockchain platform: Select a blockchain platform that aligns with your specific needs and requirements, considering factors like scalability, security, and cost.
- Develop a robust security strategy: Implement a comprehensive security strategy that addresses all aspects of blockchain implementation, including access control, key management, and data backup.
- Partner with experienced blockchain developers: Engage experienced blockchain developers to assist with the design, development, and implementation of your blockchain solution.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology offers a powerful toolkit for enhancing digital security. Its inherent immutability, transparency, and decentralization provide significant advantages over traditional centralized systems. However, it’s crucial to understand both the benefits and limitations of blockchain before implementing it. By carefully considering its applications and addressing its challenges, organizations can leverage blockchain’s potential to create more secure and trustworthy digital ecosystems. The question remains: how will your organization harness the power of blockchain to navigate the evolving landscape of digital security and build a more resilient future?
Conclusion
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insight into Understanding the Role of Blockchain in Digital Security. We hope you found this article informative and useful. See you in our next article!






